Naypyidaw, Myanmar: A Capital Devoid of Protests
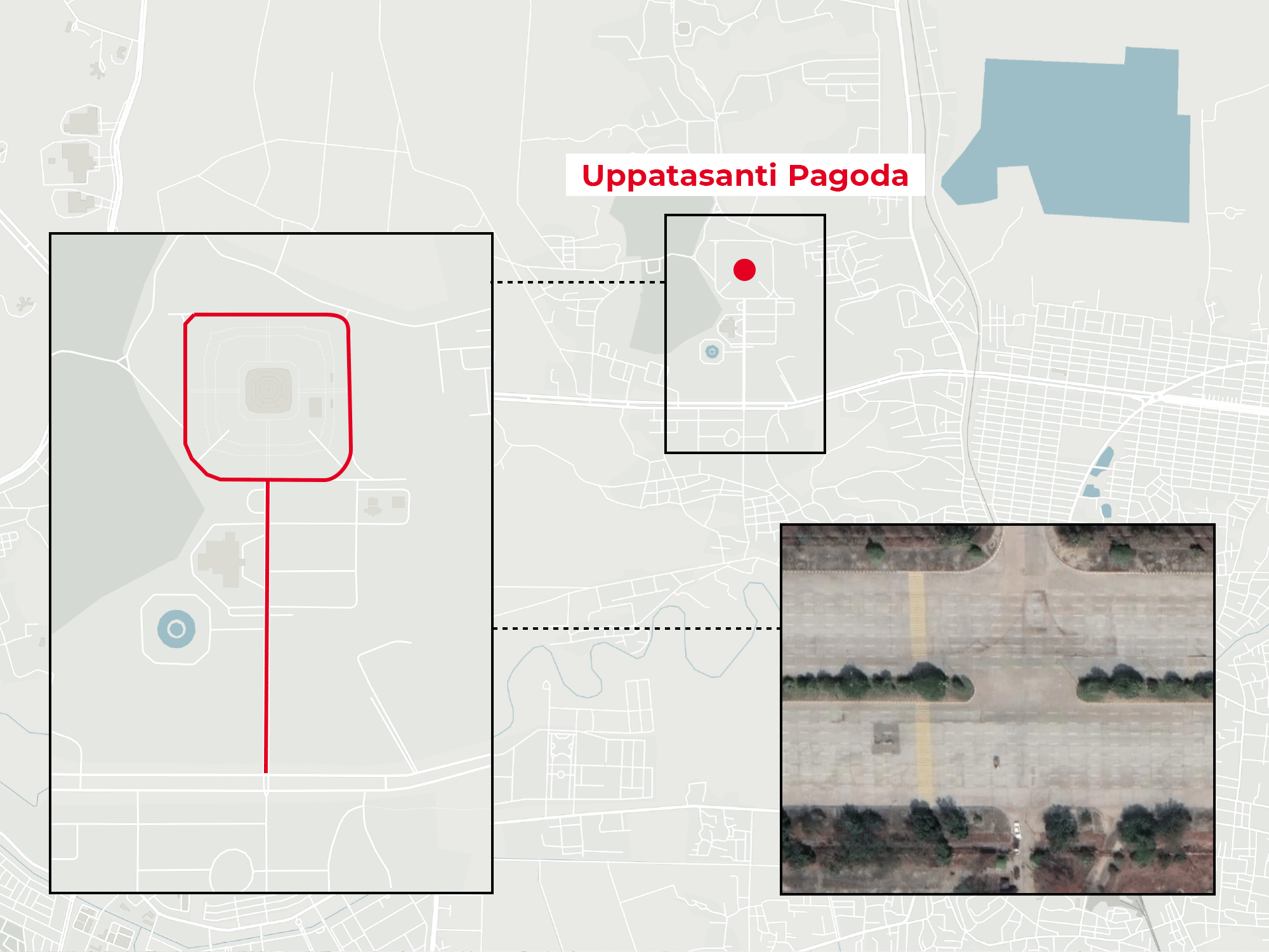
Figure 4 – The location of the Uppasanti Pagoda makes it difficult for protesters to escape from the police


After 70 years of existence, human rights are facing criticism from many sides, some even claiming their fundamental inadequacy for the 21st century or imminent end. The human rights regime, based on the Universal Declaration of Human Rights (1948) and several subsequent covenants, is variously being accused of being elitist, Eurocentric and/or imperialistic in its universal claims and remaining blind to local customs and cultural specificities; of being implemented too tamely, inconsistently or even counterproductively by International organisations that are frequently co-opted by powerful state interests; and of being unable to address fundamental societal issues and transformations such as inequality, digital transformations and climate change.
Further critiques castigate human rights’ unmet promises, framing them as a neoliberal smokescreen, or admonishing their anthropocentrism, overlooking the rights of animals, plants or other non-human entities such as robots. In such a state of flux and uncertainty, human rights have also become, to some extent, victims of their own success, being articulated not only by an increasing armada of human rights actors and activists but also by atavistic forces referring to them more cynically. Such inflationary use of human rights, increasingly following a logic of transversality as reflected in the ever-expanding UN human rights issues or the flourishing of corporate CSR strategies and codes, ultimately risks eroding their operability and epistemic traction.
However, as shifting geostrategic constellations, the rise of populism, identitarian politics, authoritarian governments and the current epidemic are all contributing to further fragilising human rights, they remain more crucial to the world’s future than ever. The current Dossier therefore asks how the human rights regime will likely evolve faced by such challenges. Can it reinvent itself and, if so, how? Can we imagine human rights without the pretension to universalism and beyond the decline of the liberal paradigm? Are we moving towards human rights that are more collective in nature or of variable geometry? New perspectives and insights are needed from the legal, social and human sciences to answer these pivotal questions.
This dossier was produced by the Graduate Institute’s Research Office in collaboration with the Geneva Academy of International Humanitarian Law and Human Rights.
The essays in this volume are the product of a new ‘research practicum‘ course in the Department of Political Science and International Relations at the Graduate Institute in Geneva. They build on the debates on ‘Urban Morphology and violence’ to reflect on the associations between cities – their political orders and disorders – and outcomes ranging from occupation and resistance to marginalisation and containment. These texts foreshadow the possibility of centring – and challenging – the urban in our understanding of contemporary conflict, violence and peace. They are a first step in opening up a research agenda for a more textured analysis of spatial, geographical and temporal dynamics within the city in relation to violence, and, therefore, the mobilisation of spatial, temporal and visual modes of analysis. The promise is to make visible the varied roles of urban morphologies – adding to the debate on cities in and as sites of conflict.
What does the experience of combining art and science bring to the study of international relations? Why blend sensibility with reason to think about the evolution of the world? How does aesthetic and/or creative performance nourish the production of academic knowledge? If thinking about creation and integrating art with the Humanities and Social Sciences is nothing new, the challenges of the 21st century call for new analyses and creative approaches that give a voice to frequently neglected perspectives, and contribute to a more nuanced and multidimensional understanding of the world. The dialectic of art and research can be approached through the artistic dimension of the object of study, proximity to artists, experimentation with new forms of fieldwork and writing, or through the cultural mediation of the results. In this special issue of the digital magazine Global Challenges, jointly produced by the Graduate Institute of International and Development Studies (Geneva Graduate Institute) and the Centre de recherches internationales (Sciences Po), the contributors shed light on the role of art in research.