Hybrid Political Orders in Urban Settings
Map: Al-Dahiyeh in Relation to the Greater-Beirut Area
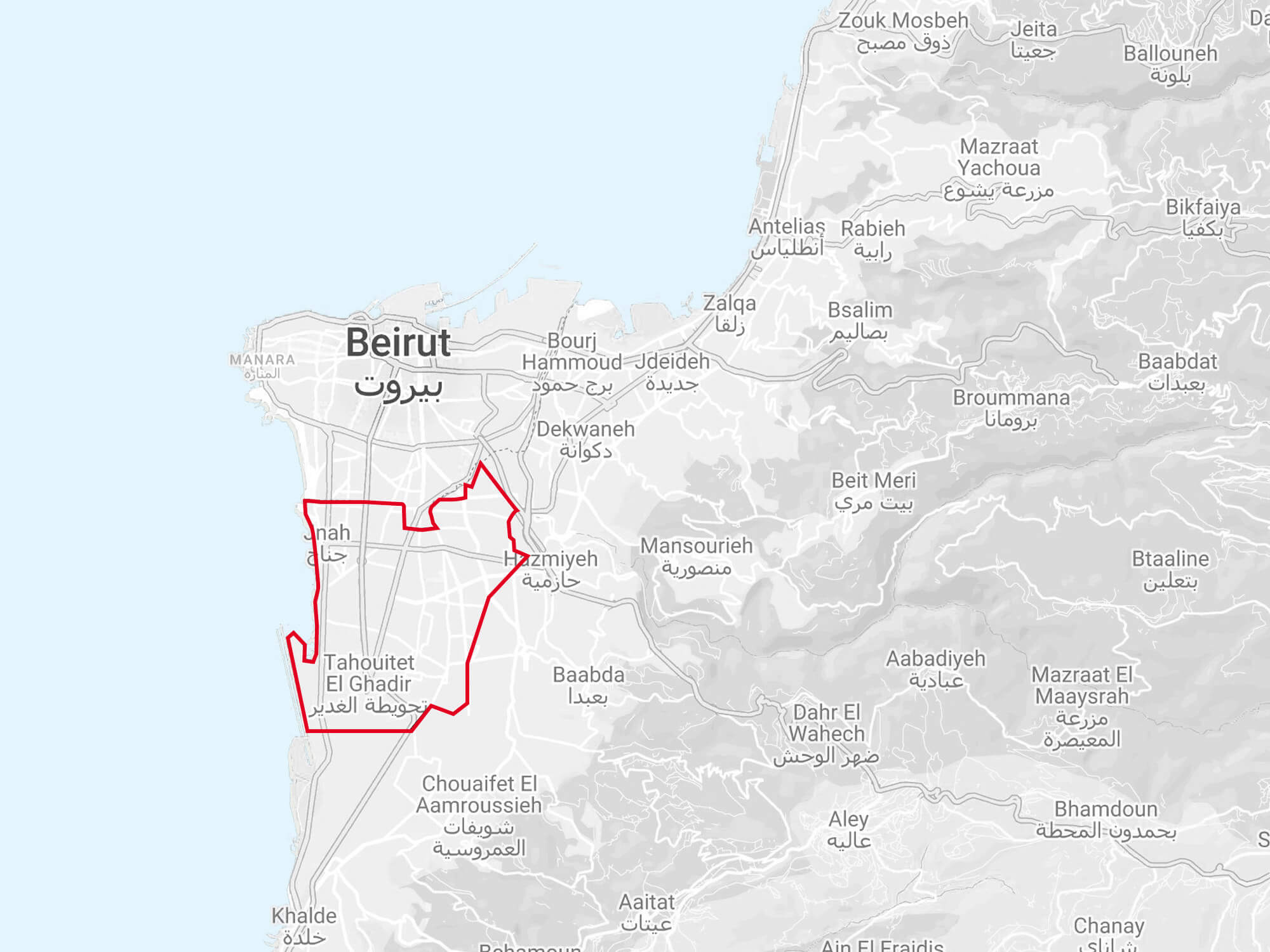
Based on Google map, by YPC.


Based on Google map, by YPC.
After 70 years of existence, human rights are facing criticism from many sides, some even claiming their fundamental inadequacy for the 21st century or imminent end. The human rights regime, based on the Universal Declaration of Human Rights (1948) and several subsequent covenants, is variously being accused of being elitist, Eurocentric and/or imperialistic in its universal claims and remaining blind to local customs and cultural specificities; of being implemented too tamely, inconsistently or even counterproductively by International organisations that are frequently co-opted by powerful state interests; and of being unable to address fundamental societal issues and transformations such as inequality, digital transformations and climate change.
Further critiques castigate human rights’ unmet promises, framing them as a neoliberal smokescreen, or admonishing their anthropocentrism, overlooking the rights of animals, plants or other non-human entities such as robots. In such a state of flux and uncertainty, human rights have also become, to some extent, victims of their own success, being articulated not only by an increasing armada of human rights actors and activists but also by atavistic forces referring to them more cynically. Such inflationary use of human rights, increasingly following a logic of transversality as reflected in the ever-expanding UN human rights issues or the flourishing of corporate CSR strategies and codes, ultimately risks eroding their operability and epistemic traction.
However, as shifting geostrategic constellations, the rise of populism, identitarian politics, authoritarian governments and the current epidemic are all contributing to further fragilising human rights, they remain more crucial to the world’s future than ever. The current Dossier therefore asks how the human rights regime will likely evolve faced by such challenges. Can it reinvent itself and, if so, how? Can we imagine human rights without the pretension to universalism and beyond the decline of the liberal paradigm? Are we moving towards human rights that are more collective in nature or of variable geometry? New perspectives and insights are needed from the legal, social and human sciences to answer these pivotal questions.
This dossier was produced by the Graduate Institute’s Research Office in collaboration with the Geneva Academy of International Humanitarian Law and Human Rights.
While poverty has been diminishing in absolute terms and relative income has been growing on a global scale for over two centuries, inequality – as measured by instruments such as the Gini coefficient – has been increasing steadily since the early 1980s. With the financial crisis of 2007, the growing digitalisation of the economy and the current pandemic, global inequality has further worsened, seeing the fortunes of the superrich attaining unprecedented levels and revenue concentrating in the top percentiles of societies.
Concurrently to the aggravation of the social fracture, additional fault lines have been opening or hardening along logics of race, gender, ethnicity and religion. Identarian revendications and logics of difference and exclusion have come to complement, compete with or supersede more traditional struggles for equality in a postmodern and neoliberal context that has normalised inequality, homogenised societies and done away with earlier grand narratives and collective agendas.
The consequences of inequality(ies) are dramatic, as reflected in the polarisation and fragmentation of societies, worsening health and mortality indicators, political tensions and violence, a decline in democracy, and mistrust in state institutions. The objective of the current issue of Global Challenges is therefore – by reverting to the analytical tools of social science – to reflect on the causes behind the multifaceted growth of inequality(ies), anticipate their noxious fallouts and explore potential remedies.
A pandemic is not just a medical emergency – it is also a political, economic, and social crisis. It implies new challenges for democratic institutions and practices, for citizenship rights and human rights as some of the restrictions on civil liberties put in place by liberal and illiberal democracies may well outlive the coronavirus. This special issue explores some tensions and dilemmas of democracies faced with the current crisis. “Politics of the Coronavirus Pandemics” addresses questions like: Can we speak of a decline in politics during the pandemic? While states have been using the full gamut of their sovereign prerogatives, has the political (temporarily) faded in the face of, for example, “expertise”? What will be the lasting impact of the rule by administrative fiat, and of emergency powers put in place in many countries? What kinds of agenda and instruments of civic activism are likely to emerge given that courts are rarely in session and public protest not permitted due to distancing rules? What are the likely consequences of these reconfigurations for democracy, governance, and welfare systems in the global South and North?