Has globalisation reached its apex after centuries of growth as suggested by the latest figures of the WTO? In the affirmative, does this imply that we are ushering into a new era of degrowth? Or are we witnessing the reorganisation of the very architecture of globalisation, which remains based on the twin logic of the acceleration and continuous increase of the volume of exchanges, as well as the steady densification of geographic connectedness. Are global exchanges restructuring concomitantly to the fourth technological revolution and the expansion of the digital economy? The present Dossier proposes to approach this question by observing the nature and the evolution of the principal flows that characterize globalisation.
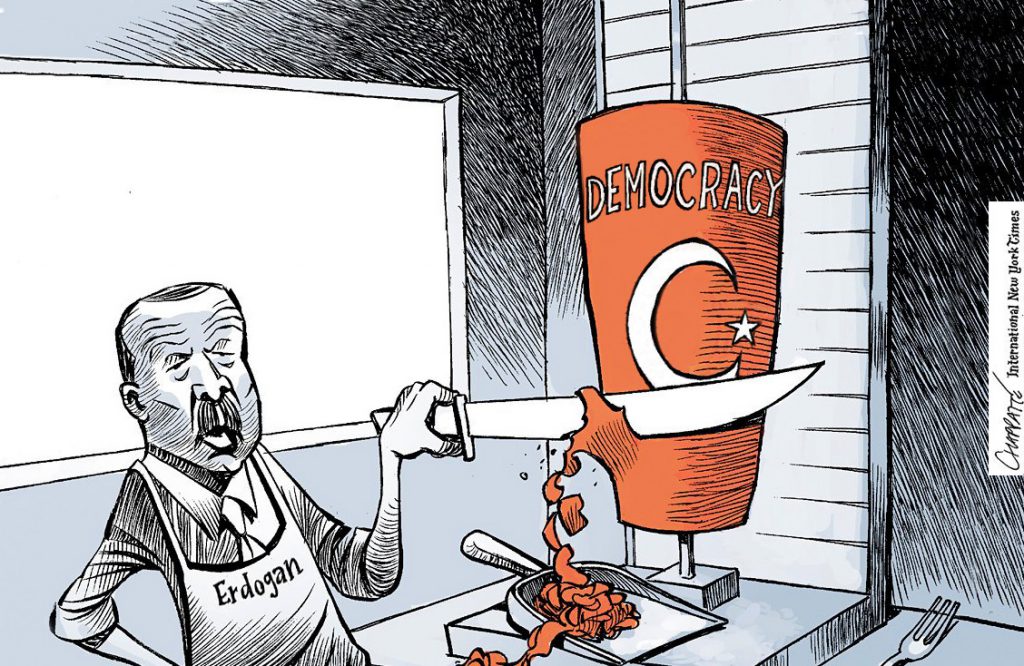
© Chappatte dans Le Temps, Genève.
In 2024, nearly half the world’s population, including citizens of the eight most populous nations, voted or will vote in elections. While this signals democratic engagement, many elections are run by autocratic or illiberal regimes pursuing self-serving agendas. Paradoxically thus, as elections are generalising as a practice, democracy is met with growing defiance. On closer scrutiny, however, it appears that it is not only the indicators of democracy but also those of elections that have been declining over the past decade. This dossier, produced with the Albert Hirschman Centre for Democracy, examines the essential role of elections in the construction of democracy today.
-
I

Do Elections Still Serve Democracy?
Reading time: 7 min -
1

European Elections 2024: The Cordon Sanitaire and the Rightward Shift
Reading time: 5 min -
2

United States: A Model Democracy under Threat?
Reading time: 5 min -
3

Debunking the Myth of “Sham Elections” in the Middle East
Reading time: 5 min -
4

Russia’s Vestiges of Democracy
Reading time: 5 min -
5

A Victory without Time to Celebrate: The Challenges for Mexico’s First Female President
Reading time: 5 min -
6

What the South African Elections Say about Its Democracy
Reading time: 6 min -
7

Democratic Challenges: The Gap between Political Platforms and Climate Concerns in Argentina
Reading time: 5 min -
8

El Salvador’s “Strongman”
Reading time: 5 min -
9

Democracy, Civil Disobedience and Populism
Reading time: 5 min -
10

Legitimacy under Pressure: The Role of Electoral Observation
Reading time: 5 min -
11

The Funding of Election Campaigns in India
Reading time: 6 min -
12

The Politics in Anti-Politically Correct Discourses
-
O

Elections and Democracy in 2024: Three Overriding Trends
Reading time: 5 min