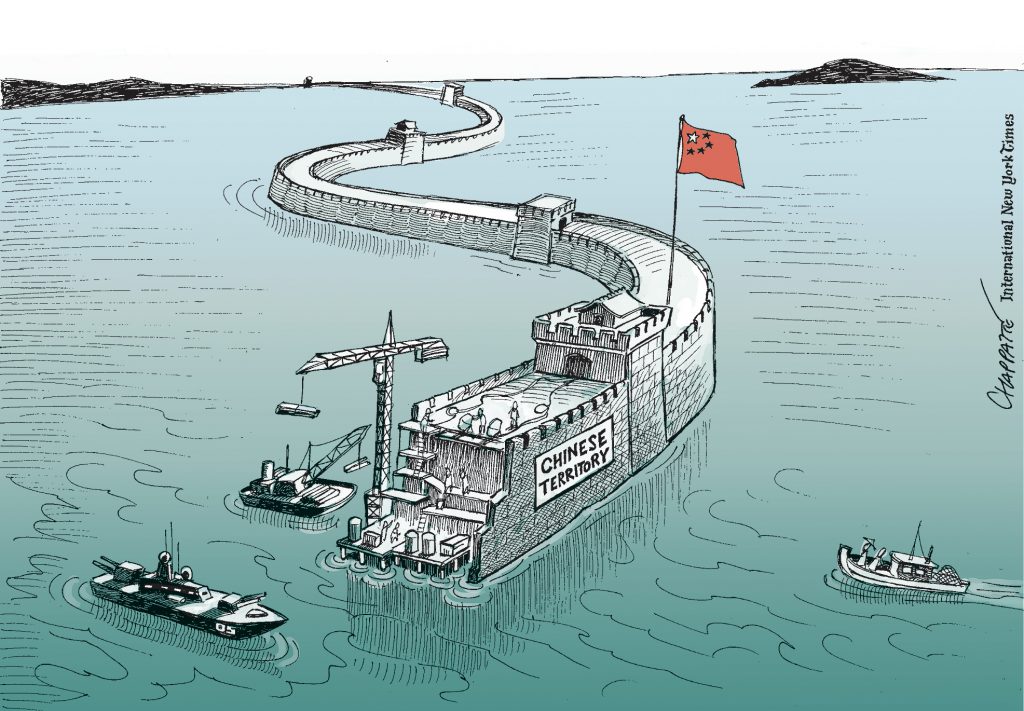
While the global balance of power, under the impetus of the steady rise of China, is shifting towards the Asia-Pacific, and because the future of US policy is uncertain after the election of Donald Trump, tensions in the South China Sea have once again become a major strategic concern. The South China Sea is witnessing a series of sovereignty disputes between littoral states defending rivalling claims to maritime rights and boundaries. Adding weight and urgency to the disputes are the significant natural resources found in the coveted archipelagos and sea beds as well as the rising national sentiments in many of the claimant states. The geostrategic dimension of these quarrels is largely transcending the region and the involvement of external powers such as the United States further complicates the equation. The recent legal victory of the Philippines over China can be seen as a supplementary cause for anxiety in a latent conflict that may at any time escalate into a regional or global confrontation. Henceforth the search for a negotiated solution becomes crucial as military budgets continue to soar in the region.
© Chappatte dans NZZ am Sonntag, Zürich
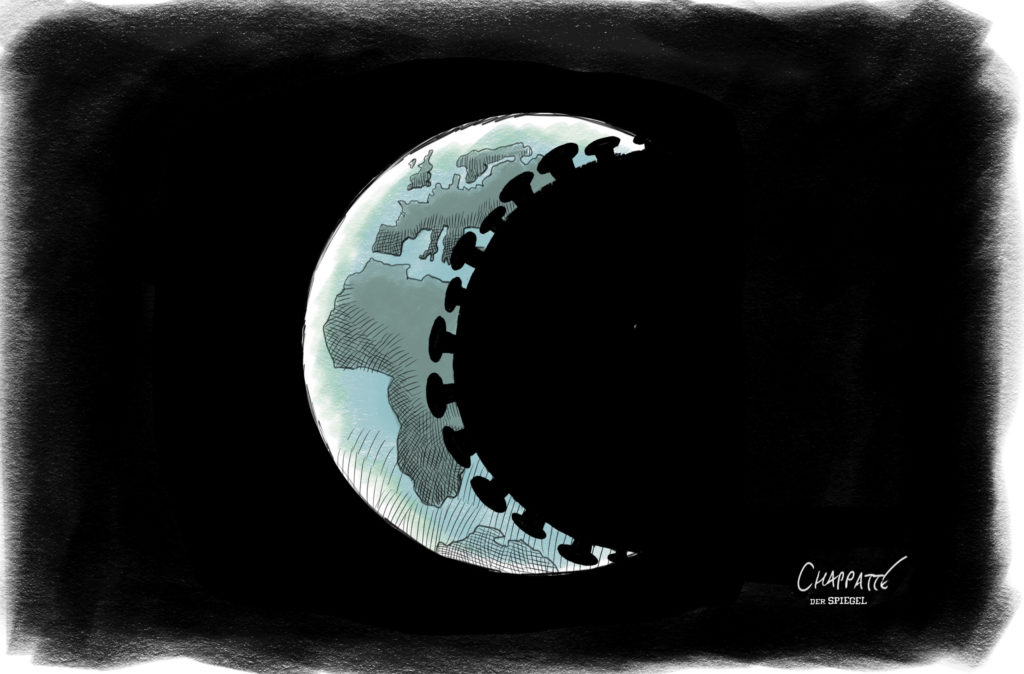
The multipolar world succeeding US hegemony in the early 21st century, the financial crisis of 2007 and the corollary decline of liberalism seem to have ushered in an era of economic nationalism. States are increasingly left to fend for themselves as multilateral mechanisms lose traction and international economic relations gain in toxicity. The sanctions, embargoes and retaliations arising from the war in Ukraine, but also an accelerating struggle for dwindling natural resources, have pushed these logics to new heights. This Dossier assesses ongoing geoeconomic transformations and their potentially devastating consequences.
-
I

War by Other Means? Geoeconomics in the 21st Century
Reading time: 6 min -
1

Globalisation: The Danger of Safe Spaces
Reading time: 4 min -
2

Risky Interdependence: The Impact of Geoeconomics on Trade Policy
Reading time: 4 min -
3

A New Page in Global Sanctions Practice: The Russian Case
Reading time: 6 min -
4

The Politicisation of the Commodities Trade
Reading time: 4 min -
5

Sanctions against Russia and the Role of the United Nations
Reading time: 4 min -
6
A Renewed Neocolonial Scramble for Resources?
Reading time: 5 min -
7

The Rise of Geoeconomics
Reading time: 5 min -
8

Debt as a Political Weapon?
Reading time: 5 min -
O

Global Sanctions: A Bibliography from the Graduate Institute
Reading time: 5 min
Dossier produced by the Research Office of the Geneva Graduate Institute.